AIV (Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles) are vehicles capable of sensing their environment, making decisions, and navigating without human intervention. These vehicles rely on Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, sensors, and real-time data processing to operate safely and efficiently.
Unlike traditional vehicles that depend entirely on human drivers, AIVs are designed to:
- Understand road conditions
- Detect obstacles and pedestrians
- Predict traffic behavior
- Take autonomous driving decisions
In simple terms, AIVs think, learn, and drive on their own.
2. How Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles Work
At the core of AIV is a decision-making AI brain that processes massive amounts of real-time data.
The basic workflow:
- Perception – Sensors scan the environment
- Interpretation – AI understands what’s happening
- Decision Making – System decides acceleration, braking, or turning
- Execution – Vehicle performs the action
All of this happens in milliseconds, faster than human reflexes.
3. Key Technologies Behind AIV

4
a. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI allows vehicles to learn from driving data, improve decision-making, and adapt to new road scenarios.
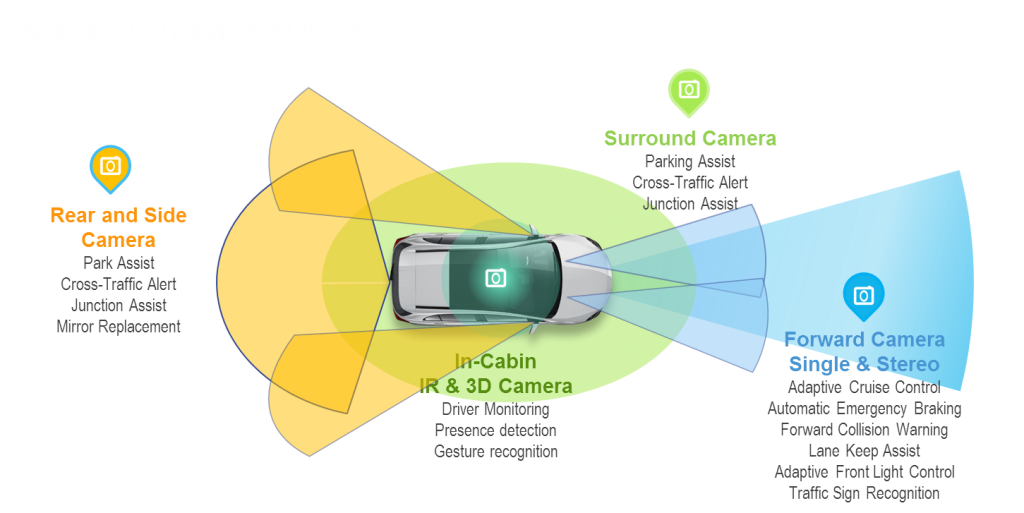
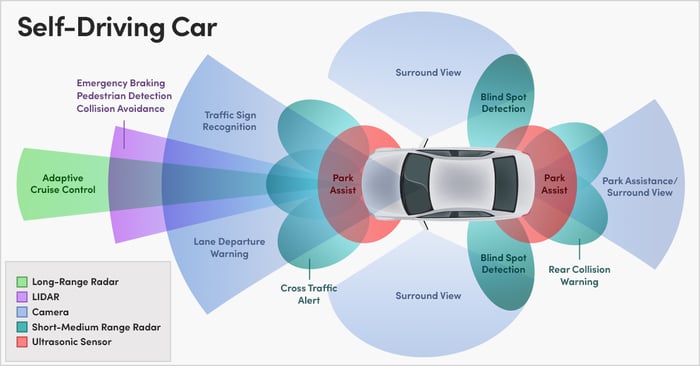
b. Sensors & Hardware
- LiDAR – 3D mapping of surroundings
- Radar – Distance and speed detection
- Cameras – Lane detection, object recognition
- Ultrasonic Sensors – Close-range awareness
c. High-Performance Computing
Powerful onboard computers process data from all sensors simultaneously.
d. HD Maps & GPS
Ultra-precise maps help vehicles understand road geometry, signals, and landmarks.
e. V2X Communication
Vehicles communicate with:
- Other vehicles (V2V)
- Traffic signals (V2I)
- Infrastructure (V2X)
Leave a Reply